What is Biogas?
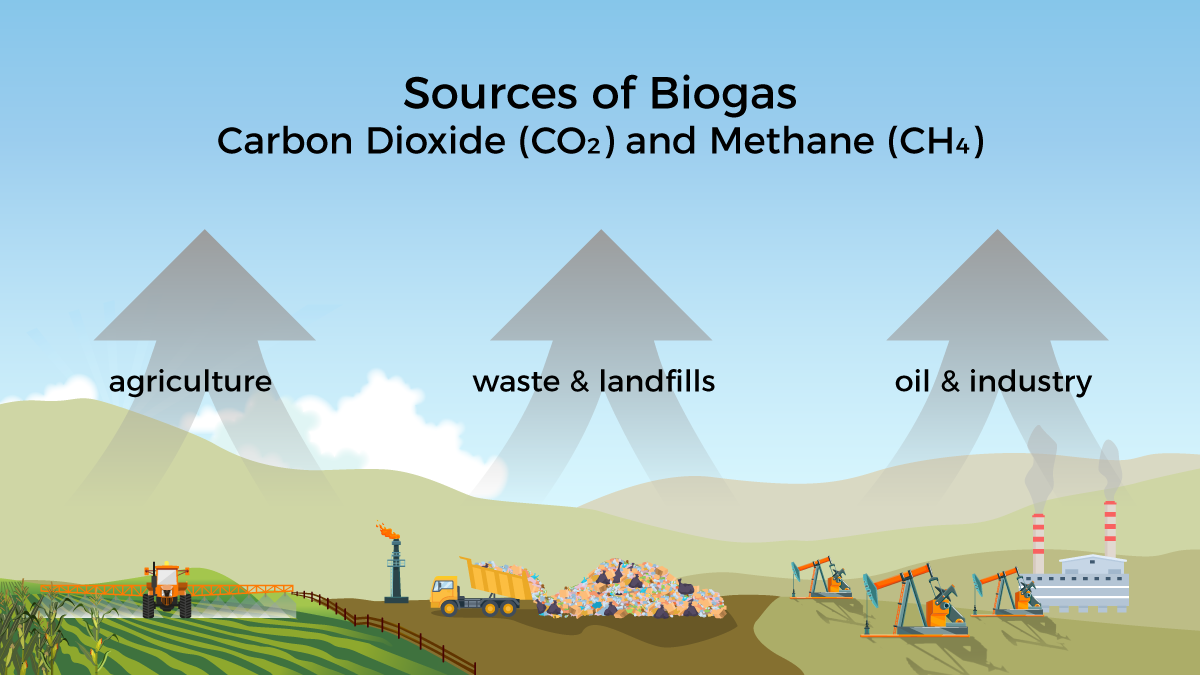
Biogas is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced as organic materials decompose in the absence of oxygen. Typical sources are landfills, water treatment facilities, manure management systems, and source separated organics such as food waste or biomass from agriculture. Biogas can be a renewable source of energy, but can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions when not responsibly managed.
Methane is a much more potent greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, so preventing methane emissions and utilizing it to produce energy (heat, electricity, vehicle fuel) can make a major contribution to the overall reduction of greenhouse gases and their impact on climate change.
Can it be useful?
Biogas from landfills can be processed into high quality natural gas to be used as an energy source; the landfill gas energy industry is now well-developed as a result of federal incentives and private investment. Other types of biogas recovery and use have not advanced as much — but policymakers at the local, state, and national level now recognize that organic waste can be a useful resource rather than simply a problem to manage.
Anaerobic digesters utilize waste from agriculture, livestock, and food to produce biogas that can be used as an energy resource. Successful biogas systems include the infrastructure to manage the waste sources, remove contaminants from the biogas, and the equipment to generate energy from the biogas.

 Carl Young, used under CC 4.0 License
Carl Young, used under CC 4.0 License